| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 가중 최소제곱법
- reflection matrix
- 추정문제#normal equation#직교방정식#정사영#정사영행렬#정사영 변환
- weighted least-squares
- 오일러-코시 미방#계수내림법
- 푸리에 정리
- 직교행렬#정규직교행렬#orthonormal#reflection matrix#dcm
- dirichlet
- 미분방정식 #선형 미분방정식 #상미분 방정식
- 비제차#제차해#일반해#적분인자#적분인자법#homogeneous sol#nonhomogeneous sol#integrating factor
- 멱급수법
- 선형독립#기저벡터#선형확장#span#basis
- 최소자승#least-square#목적함수#양한정#정점조건#최소조건
- 푸리에 급수
- 정규직교행렬
- 2계미방#모드#mod#특성방정식#characteristic eq#제차해
- 선형변환#contraction#expansions#shears#projections#reflection
- 내적#duality#쌍대성#dot product
- 내적 공간#적분
- 계수내림법#reduction of order#wronskian#론스키안#아벨항등식#abel's identity
- 부분 분수분해
- 베르누이 미분방정식
- 선형시스템연산자#라이프니츠 법칙#fundamental theorem of algebra#erf
- linespectra#feurierseries#푸리에 급수
- 여인자
- 상태천이행렬#적분인자법#미정계수법#케일리-헤밀톤 정리
- 여인수 행렬
- 선형 상수계수 미분방정식#lccode#sinusoidal input
- 그람-슈미트 과정#gram-schmidt process
- 변수분리#동차 미분방정식#완전 미분방정식
Archives
OnlyOne
Solving Non-Linear Equations 본문
Solving Non-Linear Equations
Intro
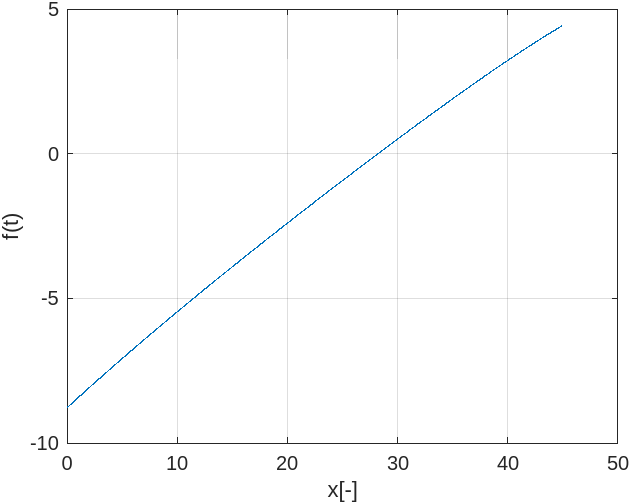
This posting will give you some methods to help you find a nonlinear equation's approximated value. Before organizing our purpose, let's see this example problem.
Example MATLAB function
%================================================
%Handong Global University
%------------------------------------------------
%Name: Taesan Kim
%ID: 22300203
%Create: 2024.09.05
%Modifire: 2024.09.05
%------------------------------------------------
%Plot of Trajectory Formula
%================================================
clc, clear all, close all;
t = 0:1e-3:45;
t0 = 3.0; %Find the most closest value with initial value 10.
sol = fzero(@fn,t0); %fzero find x which make @function = 0
axis equal;
plot(t, fn(t)); grid on
xlabel('x[-]'); ylabel('f(t)');
%Find theta which is solution of fnTrajectory = 0
disp(['Solution for t where fn = 0: ', num2str(sol), ' degrees']);
%Trajectory formula
function z=fn(t)
x=20; y=2; v=17; g=9.8;
z=x.*tand(t)-g.*x.*x./(2.*v.*v.*cosd(t).*cosd(t))-y;
end
Purpose
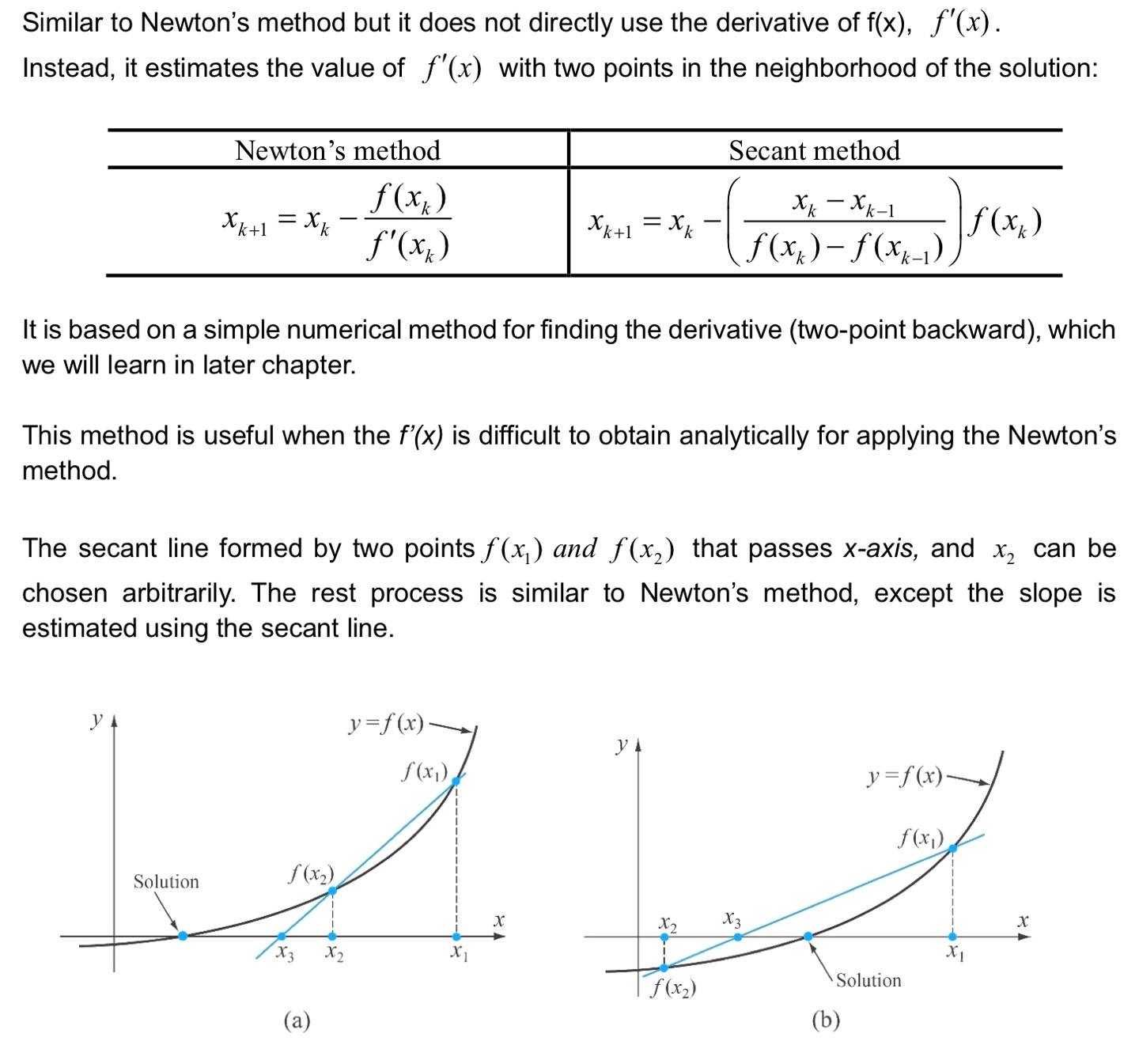
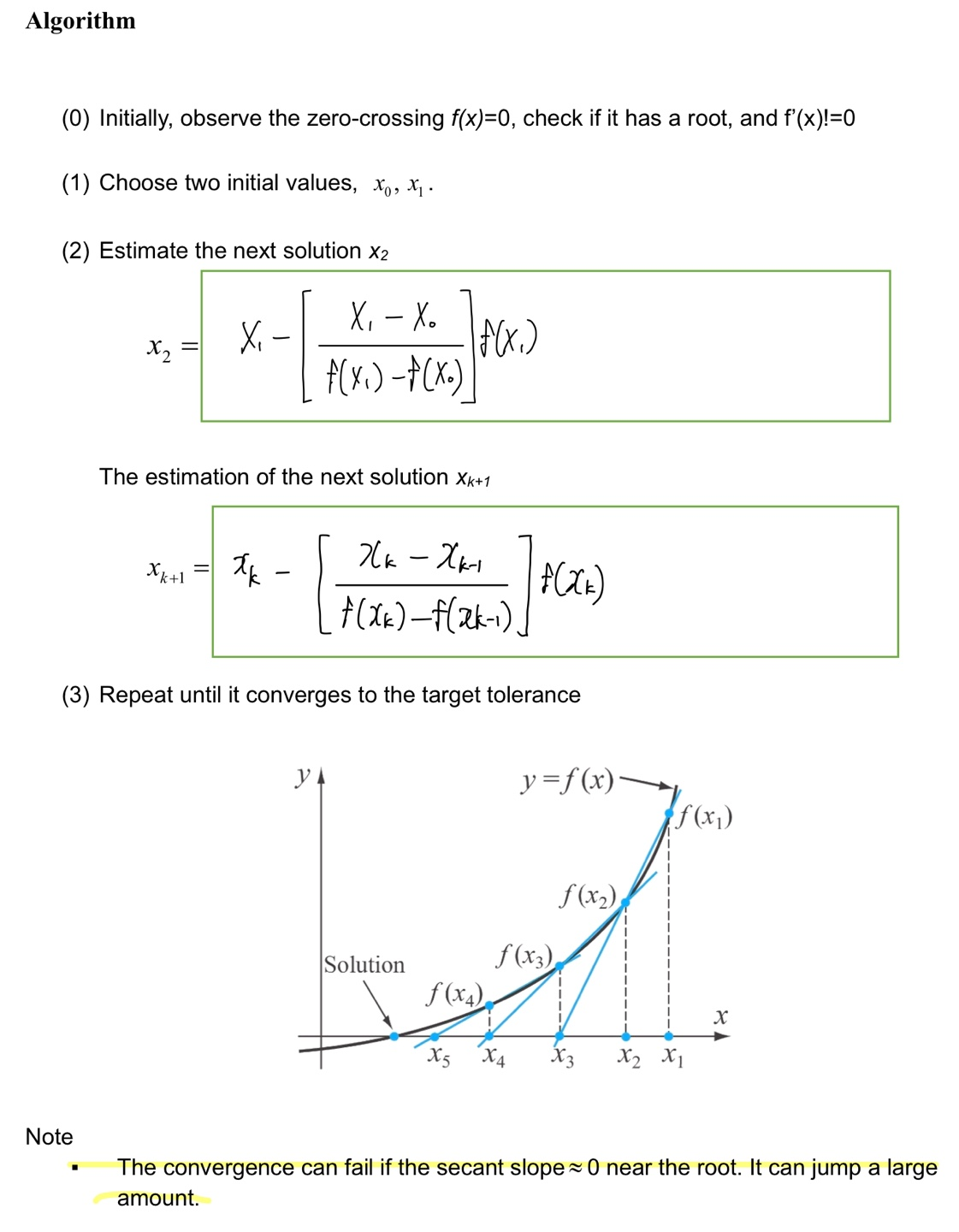
We want to derive a non-linear equation's solution not using fzero function. We will learn how to make fzero() to solve a non-linear equation with one variable, f(x) = 0. Then, we will expand the algorithm to solve a system of non-linear equations. This posting will organize 3 methods including the Bisection method, Newton-Raphson, and Secant's method.
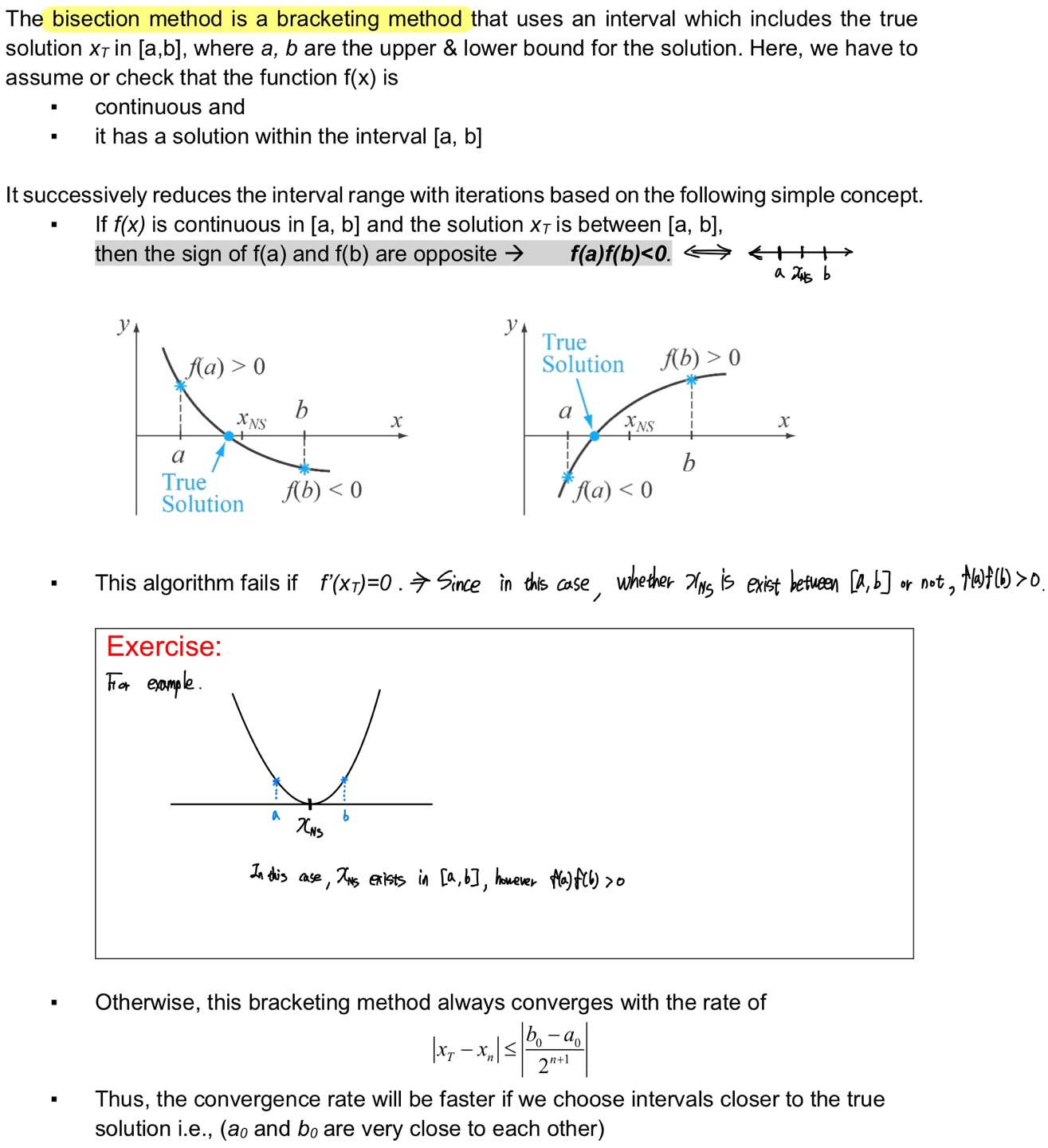
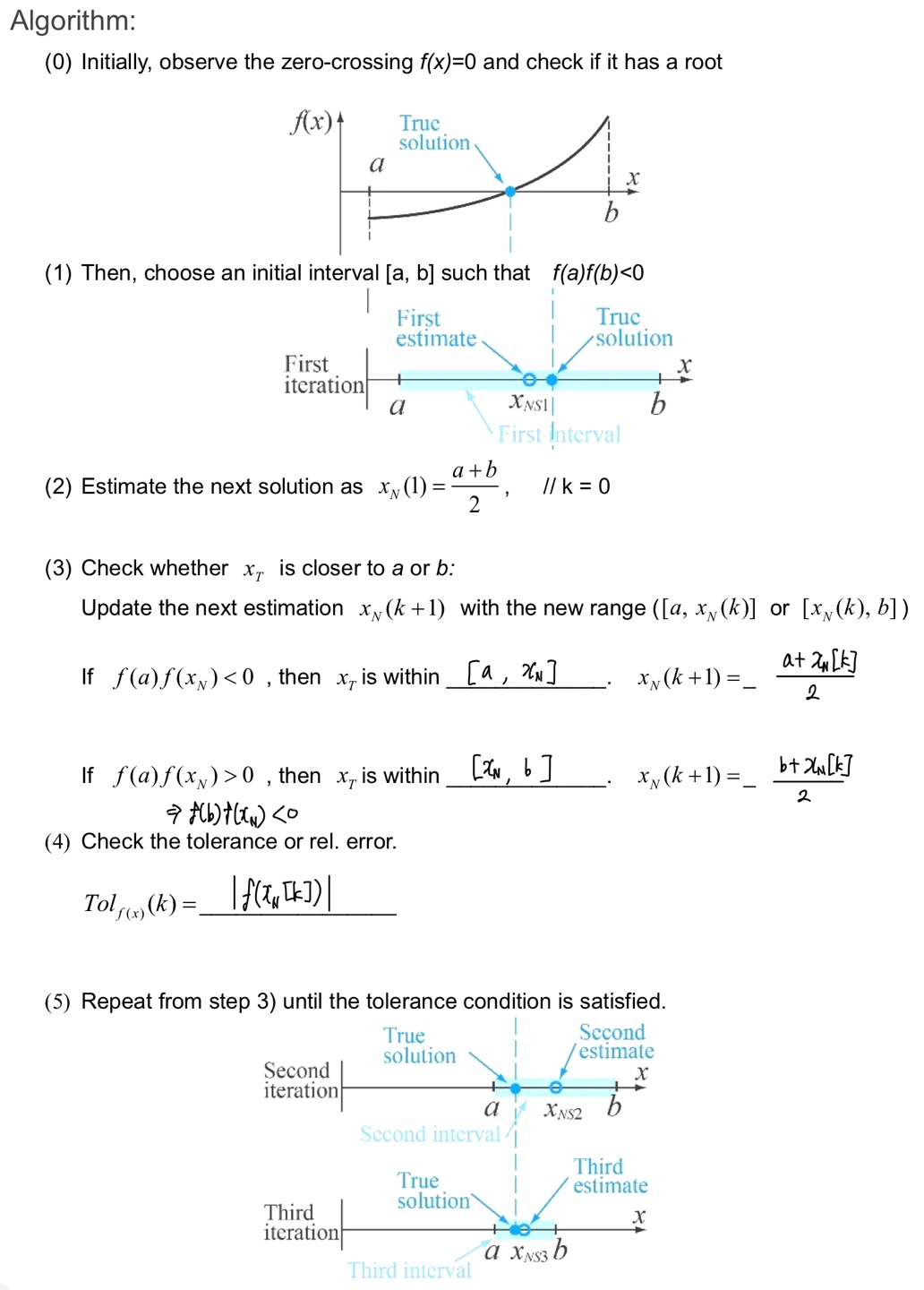
Bisection method
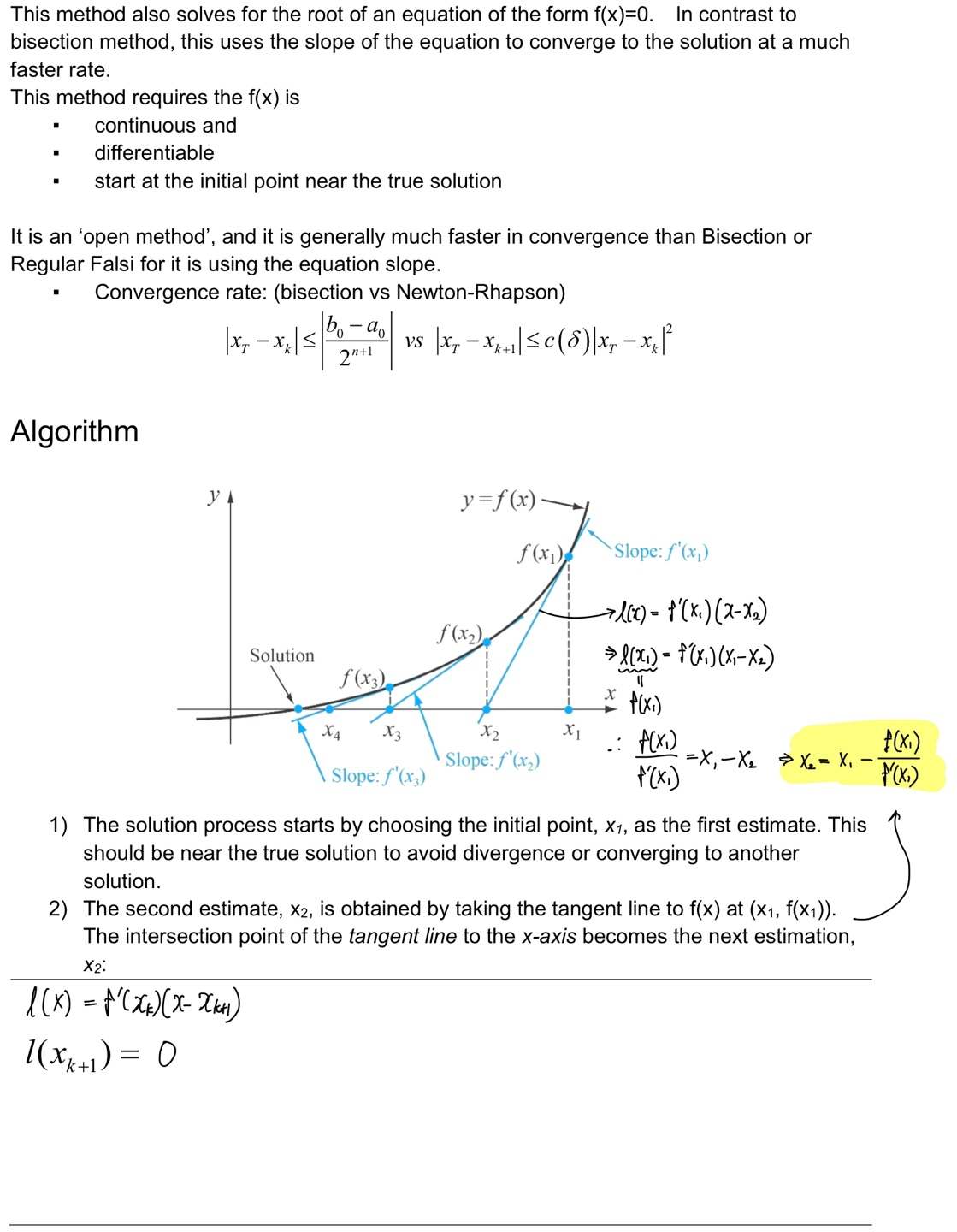
Newton-Raphson method

Secant method
Header code
/*
================================================
Handong Global University
------------------------------------------------
Name: Taesan Kim
ID: 22300203
Create: 2024.07.19
Modifier: 2024.07.19
------------------------------------------------
비선형 근삿값 계산을 지원한다.
================================================
*/
#ifndef MYNP22300203_H
#define MYNP22300203_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
/**
* Name: Non-linear approximation method newtonRaphson
* Date: 2024/09/09
* Input:
* - func: non-linear function
* - dfunc: differential non-linear function
* - x0: initial value
* - tol: allowence tolerance
* Return: None(Print error)
**/
void newtonRaphson(double func(double x), double dfunc(double x), double x0, double tol);
/**
* Name: Non-linear approximation method secant
* Date: 2024/09/09
* Input:
* - func: non-linear function
* - x0, x1: initial value
* - tol: allowence tolerance
* Return: xk
**/
float secantfzero(double func(double x), double dfunc(double x), double x0, double x1, double tol);
/**
* Name: Non-linear approximation method biSection
* Date: 2024/09/09
* Input:
* - func: non-linear function
* - tol: allowence tolerance
* - a, b: 2D area [a, b]
* Return: None(Print error)
**/
void biSection(double func(double x), double tol, double a, double b);
#endif
Source code
#include "myNP.h"
void biSection(double func(double x), double tol, double a, double b)
{
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf(" Bi-Section Method Results\n");
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf("Bi-Section Method Result:\n");
int Nmax = 1000;
double ep = 10.0;
double xk = 0.0;
int i = 0;
if (func(a) * func(b) > 0)
printf("Solution dont exists in this area!");
else
while (Nmax > i && ep > tol)
{
xk = 0.5 * (a + b);
if (func(a) * func(xk) < 0)
{
b = xk;
}
else
{
a = xk;
}
i++;
ep = fabs(func(xk));
printf("Iteration: %2d Xn(k): %f Tolerance: %f\n", i, xk, ep);
}
if (i == Nmax) printf("Solution did not converge !!!");
printf("Final Solution: %f\n", xk);
}
void newtonRaphson(double func(double x), double dfunc(double x), double x0, double tol)
{
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf(" Newton-Raphson Method Results\n");
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf("Newton-Raphson Method Results:\n");
int Nmax = 10000;
double ep = 10.0;
double xk = x0;
double h = 0.0; int i = 0;
while (i<Nmax && ep> tol)
{
if (dfunc(xk) == 0) printf("Error!! dF=0 !!");
h = -func(xk) / dfunc(xk);
xk = xk + h;
i++;
ep = fabs(func(xk));
printf("Iteration: %2d Xn(k): %f Tolerance: %f\n", i, xk, ep);
}
if (i == Nmax) printf("Solution did not converge !!!");
printf("Final Solution: %f\n", xk);
}
float secantfzero(double func(double x), double dfunc(double x), double x0, double x1, double tol)
{
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf(" Secant Method Results\n");
printf("===================================================================\n");
printf("Secant Method Results:\n");
//initialize
double xk = x0; //최종 xk를 구해준다.
double temp = 0.0;
double ep = 10.0;
int Nmax = 1000; int i = 0;
while (ep > tol && i < Nmax)
{
if ((func(x1) - func(x0)) * func(x1) == 0)
{
printf("Error!! dF=0 !!");
break;
}
temp = xk;
xk = x1 - (x1 - x0) / (func(x1) - func(x0)) * func(x1);
x0 = x1;
x1 = temp;
i++;
ep = fabs(func(xk));
printf("Iteration: %2d Xn(k): %f Tolerance: %f\n", i, xk, ep);
}
return xk;
printf("Final Solution: %f\n", xk);
}
Main code
#include "../../include/myNP.h"
#define pi 3.141592653589793238462643383279
/**
* Name: example non-linear function
* Date: 2024/09/09
* Input: x
* Return: function output
**/
double func(double x)
{
//return 8 - 4.5 * (x - sin(x));
x = x * pi / 180; // deg2rad
return 20 * tanf(x) - 9.8 * 200 / (17*17 * cosf(x)*cosf(x))-2;
}
/**
* Name: example non-linear differential function
* Date: 2024/09/09
* Input: x
* Return: differential function output
**/
double dfunc(double x)
{
//return -4.5 * (1 - cos(x));
return 20 * (1/cosf(x)) * (1/cos(x)) - 9.8 * 400 * tanf(x) * (1/cosf(x)) * (1/cosf(x)) /289;
}
int main()
{
biSection(func, 1e-5, 20,30);
newtonRaphson(func, dfunc, 28, 1e-5);
printf("%f", secantfzero(func, dfunc, 29, 30, 1e-5));
}*you should set your myNP.cpp, myNP.h file in the include folder.
'Mathematics > Numerical Method' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Numerical Solution Error and Taylor Series (1) | 2024.09.05 |
|---|

